Motion correction for MRI
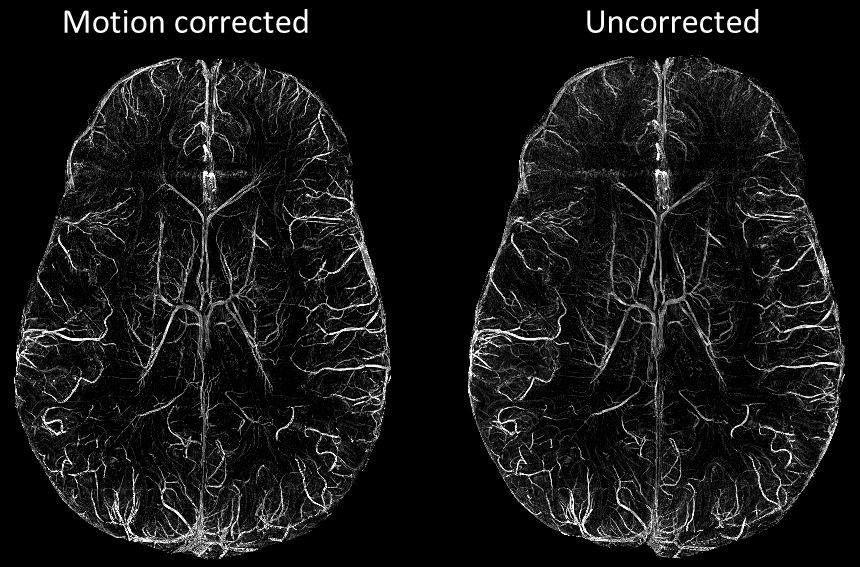
Motion is one of the archenemies of MRI. While the field of motion correction is usually concerned with making non-diagnostic images diagnostic, even compliant volunteers move unintentionally due to breathing and muscle relaxation. For (ultra-)high resolution MRI, this unintentional motion has an amplitude on the order of the voxel size. Hence, effectively reduced resolution due to motion-induced blurring is the consequence.
To overcome this inevitable resolution limit motion tracking and subsequent correction with high precision is required. I have worked extensively with prospective motion correction using an optical, MR-compatible tracking system, but also have used fat navigators with retrospective correction. While motion is an essential thread to (ultra-)high resolution MRI, it can be addressed with motion correction and we have achieved images with up to 140 µm isotropic resolution in vivo. Note that the optimal motion correction approach depends on the study at hand.
Scientific contribution & selected publications
- Book chapter and review of motion correction for ultra-)high resolution MRI.
Mattern H, Lüsebrink F, Speck O. High Resolution Structural Brain Imaging. in Motion Correction in MR: Correction of Position, Motion, and Dynamic Field Changes edited by van der Kouwe A and Andre J (2022); ISBN: 9780128244609
- Leveraging PMC to image pial arteries at 140 µm isotropic resolution.
Bollmann S, Mattern H, Bernier M, Robinson SR, Park D, Speck O, Polimeni JR. Imaging of the pial arterial vasculature of the human brain in vivo using high-resolution 7T time-of-flight angiography. eLife, 2022 DOI: 10.7554/eLife.71186
- Prospectively motion-corrected layer-specific fMRI
Iamshchinina P, Kaiser D, Yakupov R , Hänelt D, Sciarra A, Mattern H, Lüsebrink F, Düzel E, Speck O, Weiskopf N, Cichy R. Perceived and mentally rotated contents are differentially represented in cortical layers of V1. Communications Biology, 2021 DOI: 10.1038/s42003-021-02582-4
- Studying the improvement provided by PMC in 21 volunteers for multi-contrast 7T MRI.
Sciarra A, Mattern H, Yakupov R, Chatterjee S, Oeltze-Jafra S, Speck O. Quantitative Evaluation of Prospective Motion Correction in Healthy Subjects at 7T MRI. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 2021 DOI: 10.1002/mrm.28998
- Leveraging PMC to create the human phantom: an openly available high resolution dataset.
Lüsebrink F, Mattern H, Yakupov R, Acosta-Cabronero J, Ashtarayeh M, Oeltze-Jafra S, Speck O. Comprehensive ultrahigh resolution whole brain in vivo MRI dataset as a human phantom. Scientific Data, 2021 DOI: 10.1038/s41597-021-00923-w
- Comparing Fat navigators and the MPT tracking system for high resolution motion correction.
Gretsch F, Mattern H, Gallichan D, Speck O. Fat navigators and Moiré phase tracking comparison for motion estimation and retrospective correction. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 2019 DOI: 10.1002/mrm.27908; *joint first author
- Improving QSM and QSM-based venograms at 7T with PMC. and QSM Study
Mattern H, Sciarra A, Lüsebrink F, Acosta-Cabronero J, Speck O. Prospective motion correction improves high resolution quantitative susceptibility mapping at 7T. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 2018 DOI: 10.1002/mrm.27509
- PMC improves vessel depiction in high resolution ToF angiography acquired at 7T
Mattern H, Sciarra A, Godenschweger F, Stucht D, Lüsebrink F, Rose G, Speck O. *Prospective motion correction enables highest resolution time-of-flight angiography at 7T.+ Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 2017 DOI: 10.1002/mrm.27033
- Using PMC to acquire MPRAGE data at 250 µm at 7T
Lüsebrink F, Sciarra A, Mattern H, Yakupov R, Speck O. T1-weighted in vivo human whole brain MRI dataset with an ultrahigh isotropic resolution of 250 µm. Scientific Data, 2017 DOI: 10.1038/sdata.2017.32
Open source and publicly available data
- A rotation device for cross-calibration of the MPT system at 7T. The CAD model (as STEP file) of the remotely controllable rotation device is provided here and is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/ or send a letter to Creative Commons, PO Box 1866, Mountain View, CA 94042, USA. Published in:
Thoma N, Odenbach R, Mattern H, Friebe M. Remotely controllable phantom rotation system for ultra-high field MRI to improve Cross Calibration. Current Directions in Biomedical Engineering, 2019 DOI: 10.1515/cdbme-2019-1570538325